手写vue源码之vue-router路由附源码下载
日期:2020-08-15
来源:程序思维浏览:2616次
Vue Router的两种模式
hash模式实现原理
History模式实现原理
Vue Router的使用
vue作为一个渐进式框架取决于它有强大的插件机制,通过注册对应的插件得到想要的功能.
Vue.use可以接受一个对象类,调用类中的静态方法install实现功能. 也可以接受一个函数并直接调用.
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
// 1. 注册路由插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 2. 创建 router 对象
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
new Vue({
// 3. 注册 router 对象
router,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
类图
根据类图中提供的属性和方法去实现对应的功能,能让我们的目标更加清晰.
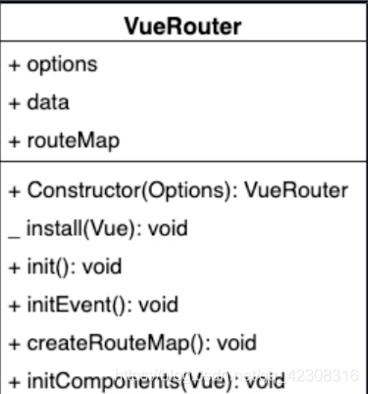
如上可见,这个名为VueRouter的类它有三个属性和六个方法.其中+号是对外公开的代码,_号是静态方法.
三个属性:
options属性是记录构造函数传入的对象,比如记录我们在new VueRouter的时候传入的routes对象规则;
routeMap是一个对象用来记录路由地址和组件的对应关系,将来我们会将options对应到routeMap中来.
data是通过vue.obsverber存储响应式数据的,因为路由地址更改过户对应的组件要更新. 它里边有一个属性current是用来记录当前路由地址的
六个方法:
install是一个静态方法,用来实现vue的插件机制;
Constructor构造函数是用来初始化对应的属性;
init用来初始化功能方法;
initEvent是用来注册popState事件监听浏览器历史的变化;
createRouteMap是用来初始化routeMap属性的把传入的路由规则转换成键值对的形式存储到routeMap中去,键是路由的地址,值是路由的组件;
initComponents是用来创建和这两个组件的.
具体实现
这里我们主要实现历史模式
install方法实现
install当Vue.use(VueRouter)时会被调用,它是一个静态方法,用来实现vue的插件机制,它接收一个Vue对象.通过Vue对象的mixin能在第一次实例化的时候拿到router.并实现路由方法的初始化.
let _Vue = null
export default class VueRouter {
static install (Vue) {
// 1.判断当前插件是否已经被安装
if (VueRouter.install.installed) return
VueRouter.install.installed = true
// 2.把Vue构造函数记录到全局变量
_Vue = Vue
// 3.把创建Vue实例时传入的router注入到_Vue上. 混入
_Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate () {
if (this.$options.router) {
// 创建的时候vue肯定是可以拿到router的 这个时候把它给_Vue的原型
_Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router
this.$options.router.init()
}
}
})
}
init () {
//初始化方法
}
}
注意this.$options拿到的是Vue初始化时传入的对象.所以接下来我们在该类中实现的所有属性和方法都能在this.$options.router中拿到.
const vm = new Vue({
router,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
constructor的实现
如下是截取路由规则与实例化代码部分代码
// 路由规则
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Index',
component: Index
},
{
path: '/blog',
name: 'Blog',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "blog" */ '../views/Blog.vue')
},
{
path: '/photo',
name: 'Photo',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "photo" */ '../views/Photo.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
routes
})
constructor接收实例化路由对象时传进来的对象,它的作用是初始化属性.
options参数就是new VueRouter时传入的对象 { mode: 'history', routes},其中routeMap是一个对象用来记录路由地址和组件的对应关系.
constructor (options) {
this.options = options
this.routeMap = {}
// observable实现current的双向绑定
this.data = _Vue.observable({
current: '/'
})
}
createRouteMap的实现
createRouteMap遍历路由规则,解析成键值对存储在routeMap中.键是路由的地址,值是路由的组件.
createRouteMap () {
this.options.routes.forEach(element => {
this.routeMap[element.path] = element.component
})
}
initComponents的实现
initComponents主要创建路由中所用到的<route-link>和<route-view>这两个组件.使用.component创建组件,render渲染组件,h函数创建目标元素或生成虚拟DOM.clickHandler用来实现路由的跳转,在历史模式中主要用到HTML5的history.pushStateAPI ,作用是改变地址不会向服务端发起请求.
initComponents (Vue) {
Vue.component('router-link', {
props: {
to: String
},
// template: '<a :href="to"><slot></slot></a>'
render (h) {
// h函数(生成的目标元素,目标元素属性,内容部分插槽)
return h('a',{
attrs : {
href : this.to
},
on : {
click:this.clickHandler
},
},[this.$slots.default])
},
methods: {
clickHandler (e) {
history.pushState({},'',this.to)
this.$router.data.current = this.to
//组织a标签的默认事件
e.preventDefault();
}
},
})
const self = this
Vue.component('router-view', {
render(h) {
// component 当前路由地址
const component = self.routeMap[self.data.current]
// h可以帮我们创建虚拟DOM
return h(component)
},
})
}
这里要注意:完整版本的Vue支持template编译 运行时不支持template如果要使用需要在vue.config.js中配置 runtimeCompiler 或者配置render函数
initEvent实现
initEvent用来注册popState事件监听浏览器历史的变化,也就是点击浏览器左上角回退时要更新组件
initEvent () {
window.addEventListener('popstate',()=>{
this.data.current = window.location.pathname
})
}
init初始化方法
init () {
this.createRouteMap()
this.initComponents(_Vue)
this.initEvent()
}
完整代码
let _Vue = null
export default class VueRouter {
// install是一个静态方法,用来实现vue的插件机制
static install (Vue) {
// 1.判断当前插件是否已经被安装
if (VueRouter.install.installed) {
return
}
VueRouter.install.installed = true
// 2.把Vue构造函数记录到全局变量
_Vue = Vue
// 3.把创建Vue实例时传入的router注入到_Vue上. 混入
_Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate () {
// 只需要在实例化的时候执行
if (this.$options.router) {
// const vm = new Vue({
// 注册 router 对象
// router,
// render: h => h(App)
// }).$mount('#app')
// 实例化的时候 new Vue中的对象都放在$options中去了. 所以该类中所有属性方法都能在this.$options.router中拿到.
_Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router
this.$options.router.init()
}
}
})
}
// 构造函数初始化 属性值
constructor (options) {
// options是实例化路由对象时传进来的对象
// {
// mode: 'history',
// routes
// }
// 是记录构造函数传入的对象,比如记录我们在new VueRouter的时候传入的routes对象规则;
this.options = options
// 是一个对象用来记录路由地址和组件的对应关系,将来我们会将options对应到routeMap中来
this.routeMap = {}
// 通过vue.obsverber存储响应式数据的,因为路由地址更改过户对应的组件要更新. 它里边有一个属性current是用来记录当前路由地址的
this.data = _Vue.observable({
current: '/'
})
}
init () {
this.createRouteMap()
this.initComponents(_Vue)
this.initEvent()
}
// 遍历路由规则,解析成键值对存储在routeMap中
createRouteMap () {
this.options.routes.forEach(element => {
// 键是路由的地址,值是路由的组件
this.routeMap[element.path] = element.component
})
}
// 创建<route-link>和<route-view>这两个组件
initComponents (Vue) {
Vue.component('router-link', {
props: {
to: String
},
// 注意:完整版本的Vue支持template编译 运行时不支持template如果要使用需要在vue.config.js中配置 runtimeCompiler 或者配置render函数
// template: '<a :href="to"><slot></slot></a>'
render (h) {
// h函数(生成的目标元素,目标元素属性,内容部分插槽)
return h('a',{
attrs : {
href : this.to
},
on : {
click:this.clickHandler
},
},[this.$slots.default])
},
methods: {
clickHandler (e) {
history.pushState({},'',this.to)
this.$router.data.current = this.to
//组织a标签的默认事件
e.preventDefault();
}
},
})
const self = this
Vue.component('router-view', {
render(h) {
// component 当前路由地址
const component = self.routeMap[self.data.current]
// h可以帮我们创建虚拟DOM
return h(component)
},
})
}
//initEvent 用来注册popState事件监听浏览器历史的变化
initEvent () {
window.addEventListener('popstate',()=>{
this.data.current = window.location.pathname
})
}
}
最后在路由中用上我们自己写的路由路径
...
import VueRouter from '../vueRouter/index.js' //这里
...
手写vue源码之vue-router路由附源码下载地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1-SWQTUR08SVNyGZFYAepaw 密码:cgye
hash模式实现原理
- URl中#后的内容作为路径地址
- 监听hashchange事件
- 根据当前路由地址找到对应的组件重新渲染
History模式实现原理
- 通过history.pushState()方法改变地址栏
- 监听popstate事件
- 根据当前路由地址找到对应组件重新渲染
Vue Router的使用
vue作为一个渐进式框架取决于它有强大的插件机制,通过注册对应的插件得到想要的功能.
Vue.use可以接受一个对象类,调用类中的静态方法install实现功能. 也可以接受一个函数并直接调用.
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
// 1. 注册路由插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 2. 创建 router 对象
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
new Vue({
// 3. 注册 router 对象
router,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
类图
根据类图中提供的属性和方法去实现对应的功能,能让我们的目标更加清晰.

如上可见,这个名为VueRouter的类它有三个属性和六个方法.其中+号是对外公开的代码,_号是静态方法.
三个属性:
options属性是记录构造函数传入的对象,比如记录我们在new VueRouter的时候传入的routes对象规则;
routeMap是一个对象用来记录路由地址和组件的对应关系,将来我们会将options对应到routeMap中来.
data是通过vue.obsverber存储响应式数据的,因为路由地址更改过户对应的组件要更新. 它里边有一个属性current是用来记录当前路由地址的
六个方法:
install是一个静态方法,用来实现vue的插件机制;
Constructor构造函数是用来初始化对应的属性;
init用来初始化功能方法;
initEvent是用来注册popState事件监听浏览器历史的变化;
createRouteMap是用来初始化routeMap属性的把传入的路由规则转换成键值对的形式存储到routeMap中去,键是路由的地址,值是路由的组件;
initComponents是用来创建和这两个组件的.
具体实现
这里我们主要实现历史模式
install方法实现
install当Vue.use(VueRouter)时会被调用,它是一个静态方法,用来实现vue的插件机制,它接收一个Vue对象.通过Vue对象的mixin能在第一次实例化的时候拿到router.并实现路由方法的初始化.
let _Vue = null
export default class VueRouter {
static install (Vue) {
// 1.判断当前插件是否已经被安装
if (VueRouter.install.installed) return
VueRouter.install.installed = true
// 2.把Vue构造函数记录到全局变量
_Vue = Vue
// 3.把创建Vue实例时传入的router注入到_Vue上. 混入
_Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate () {
if (this.$options.router) {
// 创建的时候vue肯定是可以拿到router的 这个时候把它给_Vue的原型
_Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router
this.$options.router.init()
}
}
})
}
init () {
//初始化方法
}
}
注意this.$options拿到的是Vue初始化时传入的对象.所以接下来我们在该类中实现的所有属性和方法都能在this.$options.router中拿到.
const vm = new Vue({
router,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
constructor的实现
如下是截取路由规则与实例化代码部分代码
// 路由规则
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Index',
component: Index
},
{
path: '/blog',
name: 'Blog',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "blog" */ '../views/Blog.vue')
},
{
path: '/photo',
name: 'Photo',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "photo" */ '../views/Photo.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
routes
})
constructor接收实例化路由对象时传进来的对象,它的作用是初始化属性.
options参数就是new VueRouter时传入的对象 { mode: 'history', routes},其中routeMap是一个对象用来记录路由地址和组件的对应关系.
constructor (options) {
this.options = options
this.routeMap = {}
// observable实现current的双向绑定
this.data = _Vue.observable({
current: '/'
})
}
createRouteMap的实现
createRouteMap遍历路由规则,解析成键值对存储在routeMap中.键是路由的地址,值是路由的组件.
createRouteMap () {
this.options.routes.forEach(element => {
this.routeMap[element.path] = element.component
})
}
initComponents的实现
initComponents主要创建路由中所用到的<route-link>和<route-view>这两个组件.使用.component创建组件,render渲染组件,h函数创建目标元素或生成虚拟DOM.clickHandler用来实现路由的跳转,在历史模式中主要用到HTML5的history.pushStateAPI ,作用是改变地址不会向服务端发起请求.
initComponents (Vue) {
Vue.component('router-link', {
props: {
to: String
},
// template: '<a :href="to"><slot></slot></a>'
render (h) {
// h函数(生成的目标元素,目标元素属性,内容部分插槽)
return h('a',{
attrs : {
href : this.to
},
on : {
click:this.clickHandler
},
},[this.$slots.default])
},
methods: {
clickHandler (e) {
history.pushState({},'',this.to)
this.$router.data.current = this.to
//组织a标签的默认事件
e.preventDefault();
}
},
})
const self = this
Vue.component('router-view', {
render(h) {
// component 当前路由地址
const component = self.routeMap[self.data.current]
// h可以帮我们创建虚拟DOM
return h(component)
},
})
}
这里要注意:完整版本的Vue支持template编译 运行时不支持template如果要使用需要在vue.config.js中配置 runtimeCompiler 或者配置render函数
initEvent实现
initEvent用来注册popState事件监听浏览器历史的变化,也就是点击浏览器左上角回退时要更新组件
initEvent () {
window.addEventListener('popstate',()=>{
this.data.current = window.location.pathname
})
}
init初始化方法
init () {
this.createRouteMap()
this.initComponents(_Vue)
this.initEvent()
}
完整代码
let _Vue = null
export default class VueRouter {
// install是一个静态方法,用来实现vue的插件机制
static install (Vue) {
// 1.判断当前插件是否已经被安装
if (VueRouter.install.installed) {
return
}
VueRouter.install.installed = true
// 2.把Vue构造函数记录到全局变量
_Vue = Vue
// 3.把创建Vue实例时传入的router注入到_Vue上. 混入
_Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate () {
// 只需要在实例化的时候执行
if (this.$options.router) {
// const vm = new Vue({
// 注册 router 对象
// router,
// render: h => h(App)
// }).$mount('#app')
// 实例化的时候 new Vue中的对象都放在$options中去了. 所以该类中所有属性方法都能在this.$options.router中拿到.
_Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router
this.$options.router.init()
}
}
})
}
// 构造函数初始化 属性值
constructor (options) {
// options是实例化路由对象时传进来的对象
// {
// mode: 'history',
// routes
// }
// 是记录构造函数传入的对象,比如记录我们在new VueRouter的时候传入的routes对象规则;
this.options = options
// 是一个对象用来记录路由地址和组件的对应关系,将来我们会将options对应到routeMap中来
this.routeMap = {}
// 通过vue.obsverber存储响应式数据的,因为路由地址更改过户对应的组件要更新. 它里边有一个属性current是用来记录当前路由地址的
this.data = _Vue.observable({
current: '/'
})
}
init () {
this.createRouteMap()
this.initComponents(_Vue)
this.initEvent()
}
// 遍历路由规则,解析成键值对存储在routeMap中
createRouteMap () {
this.options.routes.forEach(element => {
// 键是路由的地址,值是路由的组件
this.routeMap[element.path] = element.component
})
}
// 创建<route-link>和<route-view>这两个组件
initComponents (Vue) {
Vue.component('router-link', {
props: {
to: String
},
// 注意:完整版本的Vue支持template编译 运行时不支持template如果要使用需要在vue.config.js中配置 runtimeCompiler 或者配置render函数
// template: '<a :href="to"><slot></slot></a>'
render (h) {
// h函数(生成的目标元素,目标元素属性,内容部分插槽)
return h('a',{
attrs : {
href : this.to
},
on : {
click:this.clickHandler
},
},[this.$slots.default])
},
methods: {
clickHandler (e) {
history.pushState({},'',this.to)
this.$router.data.current = this.to
//组织a标签的默认事件
e.preventDefault();
}
},
})
const self = this
Vue.component('router-view', {
render(h) {
// component 当前路由地址
const component = self.routeMap[self.data.current]
// h可以帮我们创建虚拟DOM
return h(component)
},
})
}
//initEvent 用来注册popState事件监听浏览器历史的变化
initEvent () {
window.addEventListener('popstate',()=>{
this.data.current = window.location.pathname
})
}
}
最后在路由中用上我们自己写的路由路径
...
import VueRouter from '../vueRouter/index.js' //这里
...
手写vue源码之vue-router路由附源码下载地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1-SWQTUR08SVNyGZFYAepaw 密码:cgye
精品好课

